Video Abstract
Artificial Intelligence is one of the great technological innovations of the digital age, and in many ways it could evolve along the lines of previous technologies.
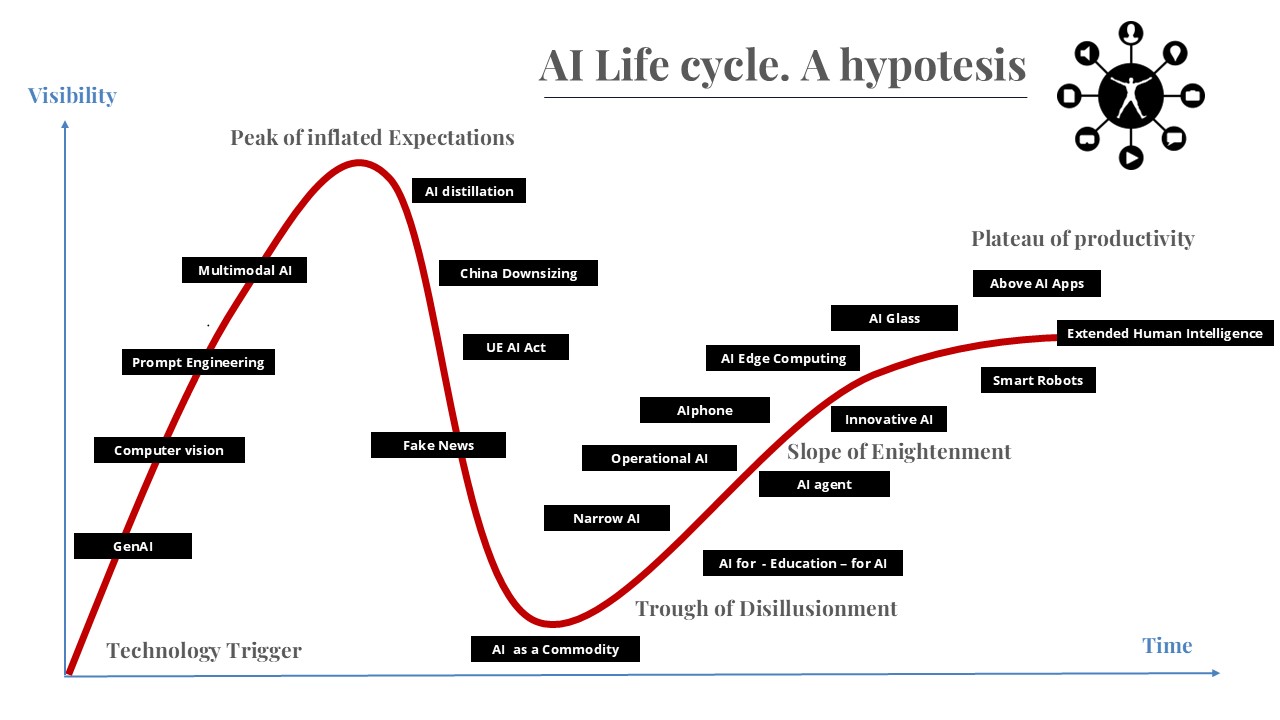
Gartner’s curve describes the stages of the cycles of technological innovations: the trigger, the peak of expectations, the disillusionment, the rise of awareness, and the plateau of productivity.
The new economy itself, and subsequent waves of innovation in the technology sector, have followed this kind of curve.
In the case of AI, the triggering of the current exponential curve is to be found in the advent of conversational technologies, particularly with the launch of ChatGPT on November 30, 2022, which sparked enormous media interest, mass adoption (hundreds of millions of users), and spectacular financial speculation that rewarded the companies involved such as Meta AI, Nvidia, Google’s Gemini, Microsoft’s Copilot, moreover, all U.S. players, and their products.
It is not known when the peak of both media and financial expectations for AI as a technological innovation will be reached, but certainly a significant transition point was the launch of the Chinese DeepSeek model on January 2025, which caused a sharp drop in the share price of chipmaker Nvidia and a sharp drop in the valuations of other U.S. technology companies. So much so that some observers said it was a “Sputnik moment” in the Chinese-American race for supremacy in the field of Artificial Intelligence. Using distillation technologies and other innovative approaches, DeepSeek has replicated the performance of U.S. models with far fewer resources, accelerating the trend of AI becoming a kind of Commodity.
The enactment of the AI Act, the European regulation on the industry, may also be a transition point to another phase, leading to the descent of the Gartner curve toward marked disillusionment following the imposition of regulatory limits on the unchecked expansion of AI. Positive media attention (media hype) may be undermined by the negative effects of multimodal AI, which will flood the infosphere with fake news and content of questionable quality. The lack of mass literacy and training in the use of AI, both in end users and in the professional sector, may also be a factor in slowing the adoption of the technology within families, schools, institutions and businesses.
In the meantime, however, there is growing awareness of the real potential of AI-enhanced technology solutions in all sectors, which can justify a less explosive growth of the AI-related economy than that of generative AI, but more robust.
Several observers in the financial community are pointing attention not so much to the sensationalist achievements of generative and general AI, but to those of emerging specialized and operational AIs, not only in the U.S. context, which have greater application potential across all sectors.
Ongoing trends include the spread of hardware devices with preinstalled AI models that are also autonomous from large cloud platforms (edge computing, AI phones), and the proliferation of robots with built-in AI functions, across all application domains.
Some of these trends in technological innovation could trigger further Gartner curves, that is, new phases of Ai expansion other than the current one.
The image is released under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. Work by Gualtiero and Roberto Carraro – Homo Extensus. Report authors’ citation and link to original page

